Log1+x Taylor Series

22 34 Example I Taylor Series Expansion Of F X Log1 X Around The Point A T X X Course Hero
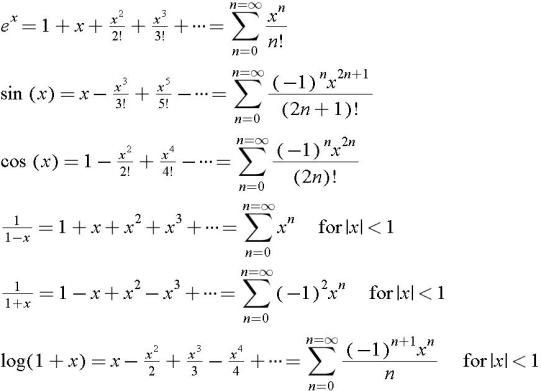
Appendix C Expansions Differentiation Integrals And Mathematical Relations Engineering360
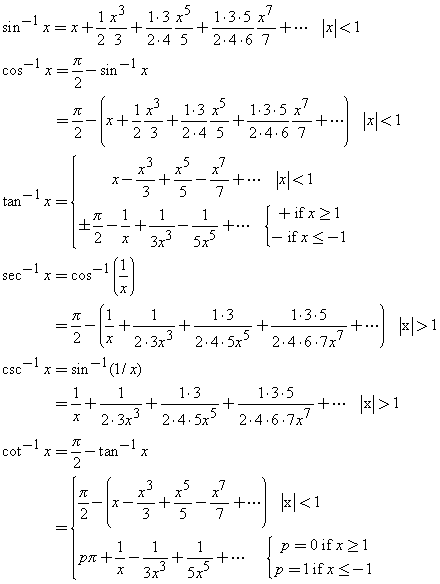
Taylor Series Expansions Of Inverse Trigonometric Functions

Expand 1 Dim Vector By Using Taylor Series Of Log 1 E X In Python Stack Overflow
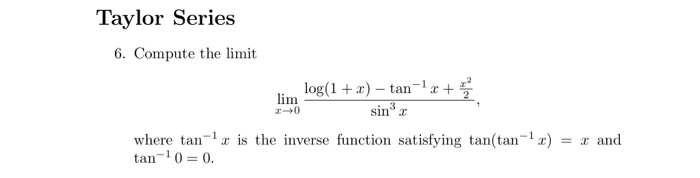
Solved Taylor Series 6 Compute The Limit Log 1 X Ta Chegg Com

Cochranmath Taylor Series Of A Function By Equating Derivatives
The Taylor Series for e x.

Log1+x taylor series. The Taylor series of a real or complex-valued function f (x) that is infinitely differentiable at a real or complex number a is the power series + ′ ()!(−) + ″ ()!(−) + ‴ ()!(−) + ⋯,where n!. If we increase the number of times the for loop runs, we increase the number of terms in the Taylor Series expansion. Arguments f differentiable function.
Compute the ( n + 1 ) th (n+1)^\text{th} ( n + 1 ) th derivative of f ( x ) :. The second degree approximation is a parabola shown in green:. Well, not quite “be mathx/math”, but “be nearly mathx/math”.
However, when the interval of convergence for a Taylor …. Series expansions of exponential and some logarithms functions. So, once the first few terms of the series are.
Free Taylor/Maclaurin Series calculator - Find the Taylor/Maclaurin series representation of functions step-by-step This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy. Compute the limit log(1 + x) – tan- lim sin where tan-' x is the inverse function satisfying tan(tan-?x) tan-10=0.
And the corresponding Taylor series for log(x) at a = 1 is and more generally, the corresponding Taylor series for log(x) at some is:. As a simple example, you can create the number 10 from smaller numbers:. In order to compute the Maclaurin polynomial of degree 4 of f(x) we will multiply out the series expansions of the functions cos(x) and ln(1 x) thus obtaining a new power series, however we will only keep those terms in the expansion of the new series that have degree at most 4.
James Gregory)가 발견했고, 1715년에 영국의 수학자 브룩 테일러(영어:. F (x) = f (a) + f ′ (a) 1!. As you can see ln1 = 0.
If you put in −1 for x the series diverges. Commonly Used Taylor Series series when is valid/true 1 1 x = 1 + x + x2 + x3 + x4 + :::. Taylor series expansions of logarithmic functions and the combinations of logarithmic functions and trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, hyperbolic, and inverse hyperbolic functions.
Graph of \ln{(x+1)} is shown in red. The result 7.0 is the same as the result we calculated when we wrote out each term of the Taylor Series individually. Actually, just to give ourselves some closure here, let's write it in sigma notation.
Log in Matlab means the natural logarithm, base e, log10 is the log base 10 The above are meant to be the natural logarithm.) (a) To get log(1.9), what value of r must be used in (1)?. The theory behind the Taylor series is that if a point is chosen on the coordinate plane (x-and y-axes. In this tutorial we shall derive the series expansion of the trigonometric function $${a^x}$$ by using Maclaurin's series expansion function.
Taylor Series & Maclaurin Series help to approximate functions with a series of polynomial functions.In other words, you’re creating a function with lots of other smaller functions. Find more Mathematics widgets in Wolfram|Alpha. A Taylor series is an idea used in computer science, calculus, chemistry, physics and other kinds of higher-level mathematics.It is a series that is used to create an estimate (guess) of what a function looks like.
= X1 n=0 17n n n!. (−),where f (n) (a) denotes the n th derivative of f evaluated at the point a. When this interval is the entire set of real numbers, you can use the series to find the value of f(x) for every real value of x.
Sounds like this question is about the Taylor series - Wikipedia of mathf(x) = \log(1+x)/math at mathx=0/math. Taylor Series A Taylor Series is an expansion of some function into an infinite sum of terms , where each term has a larger exponent like x, x 2 , x 3 , etc. Find the power series representation for g centered at 0 by differentiating or integrating the power.
Taylor computes the Taylor series approximation with the order n - 1. ( x − a )^ 2 +. Series Expansion of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions.
More variables to be passed to function f. Note how the line for i in range(10):. For the first degree approximation we get:.
(See why we want to do this in the Introduction.). In this section we will discuss how to find the Taylor/Maclaurin Series for a function. X0 point where the series expansion will take place.
Taylor Series Calculator with Steps Taylor Series, Laurent Series, Maclaurin Series. Enter a, the centre of the Series and f(x), the function. 1(x) = f(a) + f0(a)(x a) is the tangent line to f at a, the remainder R 1(x) is the difference between f(x) and the tangent line approximation of f.
Let's say we wanted a Taylor series approximation for ln(1 + x) about a = 2. Expension of log (1+x) is x - (x^2)/2 + (x^3)/3 - ( x^4)/4 +. Now includes 10.
Because the Taylor series is a form of power series, every Taylor series also has an interval of convergence. Expansions Which Have Logarithm-Based Equivalents. -+*+, = x and.
Then, the series will converge for the values of x within the interval of convergence. Deriving the Maclaurin expansion series for ln(1+x) is very easy, as you just need to find the derivatives and plug them into the general formula. Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond.
Syms x taylor(log(x), x, 'ExpansionPoint', 1) ans = x - (x - 1)^2/2 + (x - 1)^3/3 - (x - 1)^4/4 + (x - 1)^5/5 - 1. There, I described how expansions of exponentials and the trigonometric functions worked, but I didn’t have a way to expand logarithms and thus powers. The Taylor series for the exponential function ex at a = 0 is.
Logarithms of Taylor Expansions. Follow the prescribed steps. If you want to know about Taylor Series click here- Taylor series - Wikipedia.
Let's try 10 terms. Truncation order of Taylor series expansion, specified as a positive integer or a symbolic positive integer. Recognizing function from Taylor series.
Consider the following two Taylor's series log(1-x) =-ァー k-1 2k-1 (Note:. The left-hand point is -1, and. This will work for a much wider variety of function than the method discussed in the previous section at the expense of some often unpleasant work.
F ( x ) :. Find the Taylor series expansions at x = 1 for these functions. We could write the natural log of one plus x to.
A Taylor series approximation uses a Taylor series to represent a number as a polynomial that has a very similar value to the number in a neighborhood around a specified x x x value:. By integrating the above Maclaurin series we find the Maclaurin series for log(1 − x), where log denotes the natural logarithm:. X 2R cosx = 1 x2 2!.
0인 지점에서의 테일러 급수를 특별히 매클로린 급수(Maclaurin series)라 하는데, 18세기에. 1 + 2 + 3 + 4. Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving ln(x), log e (x), or log(x).
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e, where e is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718 281 8 459.The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x, log e x, or sometimes, if the base e is implicit, simply log x. (x − a) 2 + f (3) (a) 3!. Consider the function of the form \f\left( x \right).
Find the power series of ln(1+x) and use it to find the sum from n=1 to infinity of (-1)^n/n. - Geometric Series - Integration of power funct. (x − a) + f ′ ′ (a) 2!.
The rational approximation is particularly good for series with alternating terms and poor polynomial convergence like log(1+x). Cos(x)ln(1 x) for 1 < x < 1. E = 1 + 1 + 1 2!.
You can almost never find the exact value of R n(x). (Alternate signs) This proof can be generated by Taylor Series, f ( x ) = f ( a ) + f ′ ( a ) ( x − a ) + f ′ ′ ( a ) 2 !. There is also a special kind of Taylor series called a Maclaurin series.
If we want a good approximation to the function in the region near `x = a`, we need to find the first, second, third (and so on) derivatives of the function. Once you differentiate, you end up with a simple reciprocal. It can be proved that the logarithmic series is valid for x = 1.
Natural log of one plus x to the third power is x to the third power minus x to the sixth over two plus x to the ninth over three, so on and on and on. If you want to calculate log(1.9) and x=0.9 then you have apply taylor series log(1+x) see formula form google and change in to the code is. Should be n = 4 ="" code="">.
I’ve already described how Herbie computes series expansions to produce polynomial approximations to floating-point programs. E(17x) = P 1 n=0 (17 x)n!. To specify a different expansion point, use 'ExpansionPoint':.
The graph of y = 1+ 1 x looks smooth at x = 1, but there is still a problem. Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly. Finding the Taylor Series of the Log(1-x) or Log(1+x) using the Geometric Series What you should know?.
Denotes the factorial of n.In the more compact sigma notation, this can be written as ∑ = ∞ ()!. N Taylor series order to be used;. The polynomial series for exp(x) converges too well gain much benefit from Pade approximation using a first order rational polynomial.
The truncation order n is the exponent in the O-term:. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Get more help from Chegg.
Get 1:1 help now from expert Advanced Math tutors. For math, science, nutrition, history. 테일러 급수의 개념은 스코틀랜드의 수학자 제임스 그레고리(영어:.
If you put in 1, it looks like it would converge. We find the desired polynomial approximation using the Taylor Series. Note this is the geometric series.
An advantage of using a for loop is that we can easily increase the number of terms. Our aim is to find a polynomial that gives us a good approximation to some function. Just think of x as r = X1 n=0 xn x 2( 1;1) ex = 1 + x + x2 2!.
= X1 n=0 xn n!. Get the free "Log(1-x) Taylor Series" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. (2) The series expansion of log e (1 + x) may fail to be valid, if |x| is not less than 1.
+ x8 8. This is a straight line going through the origin, shown in pink. If you knew the value exactly, then you would know the precise value of f(x) (since it’s easy to compute T.
Putting x = 1 in the logarithmic series. Instead of deriving this from the formula for the geometric series we could also have computed it using Taylor’s formula. We also derive some well known formulas for Taylor series of e^x , cos(x) and sin(x) around x=0.
Brook Taylor)가 공식적으로 발표했다.

Useful Results Calculus St2 London School Of Economics Studocu

Finding The Natural Logarithm Of A Number Using Taylor Series In C Stack Overflow
What Is The Taylor Series Expansion Of Math E X Math About Zero Quora

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Taylor Series Expansions Of Logarimathic Functions
C Practical And Assignment Programs E X Series Expansion Youtube
What Is The Expansion Of Log 1 X Quora

Natural Logarithm Series

Taylor Series Expansions Of Hyperbolic Functions
Taylor Series For Log X Physics Forums

Taylor Series From Wolfram Mathworld
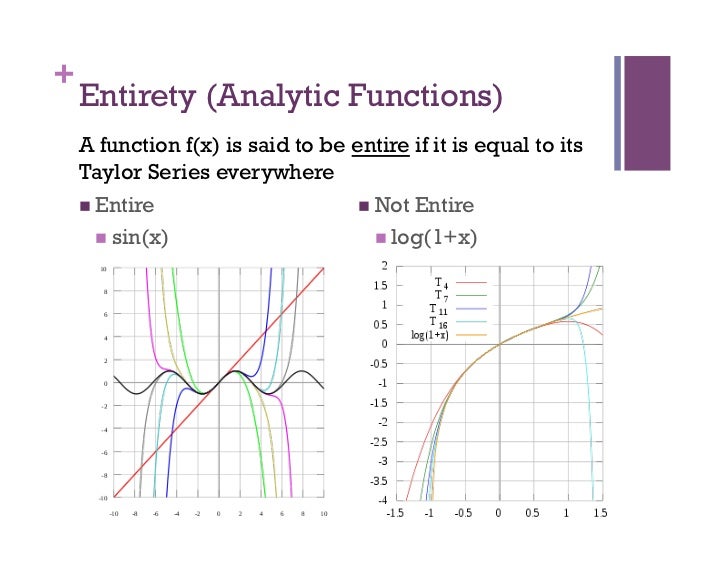
Taylor Series

Taylor Series For F X Ln X Centered At X 1 Youtube
Http Academic Uprm Edu Wrolke Esma6661 Hyp1 Html

Expand Logex In Power Of X And Hence Evaluate Loge 1 1 Correct To Four Decimal Places Answer Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection

Logarithms Logs Log Ln Lg
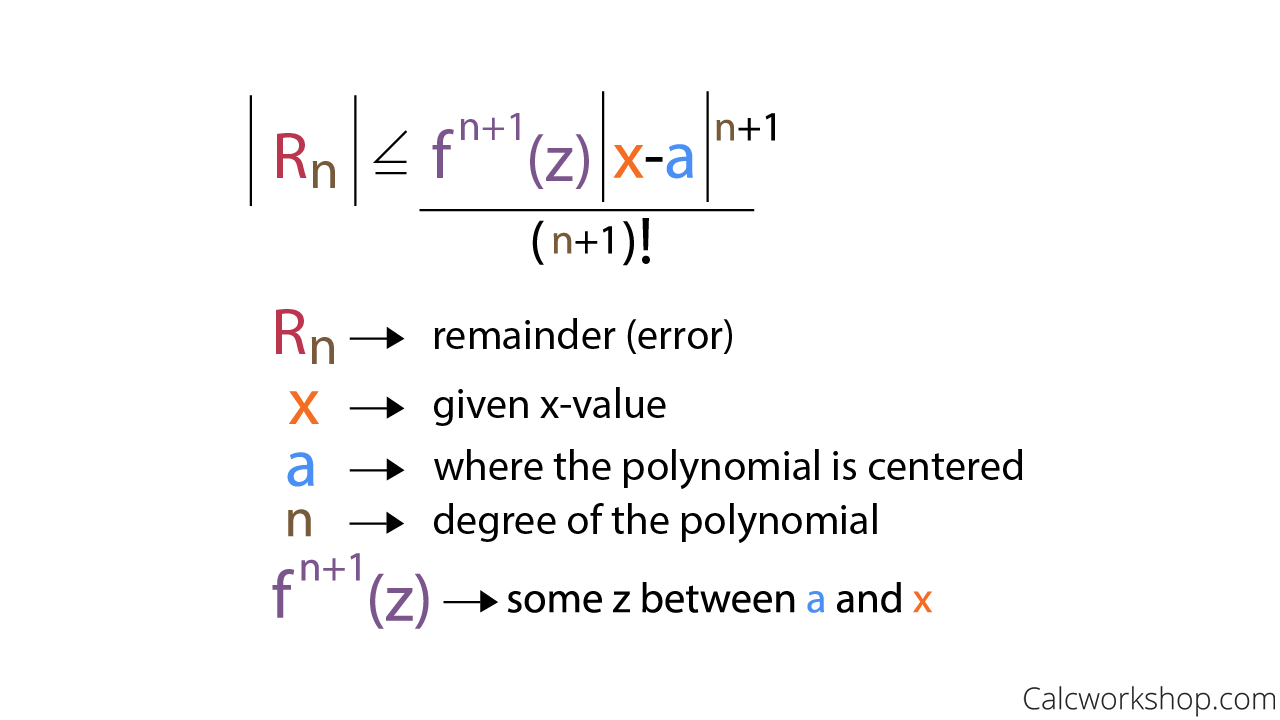
What Is Lagrange Error Bound Explained W 9 Examples

Natural Logarithm Wikipedia

Taylor Series

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Natural Logarithm Wikipedia
The Beginner Programmer Taylor Series With Python And Sympy Revised

Show That Frac 1 2 0 5 Frac 1 Frac 1 2 3 0 5 2 Frac 1 Frac 1 2 Frac 1 3 4 0 5 3 Cdots Log 2 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Taylor Series For F X Ln X Centered At X 1 Youtube

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Natural Logarithm Wikipedia

Solved 18 5 Pts The Taylor Series Approximation For Lo Chegg Com

Q Tbn 3aand9gcrkjw64ul2tgb2hw Wknvb9va5ivji2nfszfa Usqp Cau
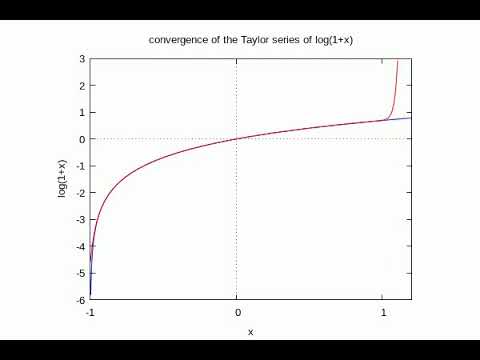
Convergence Of The Taylor Series Of Log 1 X Youtube

Taylor Series Numerical Methods Projects
Expand Log X In Powers Of X 1 By Taylor S Series Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
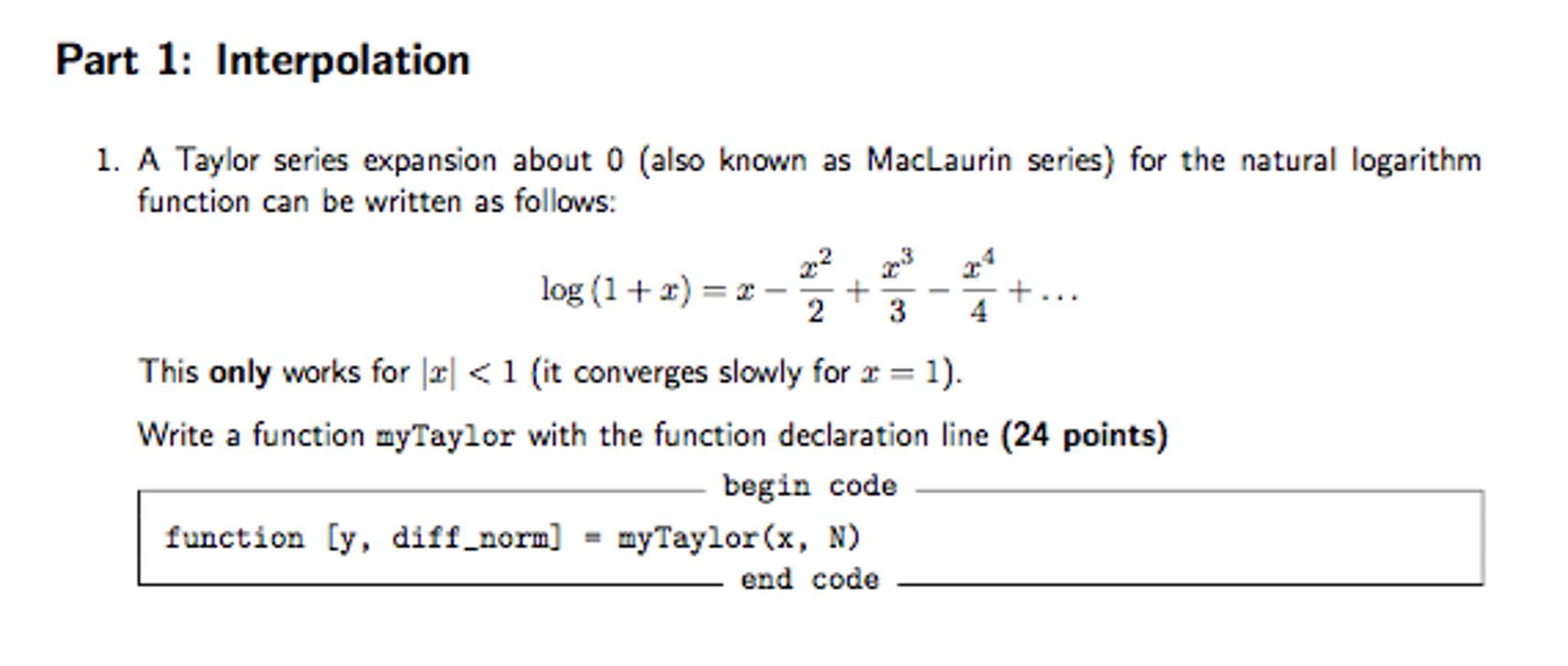
Solved Matlab Problem A Taylor Series Expansion About 0 Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gctmarfymdtysvt1crjq5gos98x03 La9hr6khunnyqvib7oix Usqp Cau

Taylor Polynomial Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Maclaurin Series For Ln 1 X Youtube

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Taylor Series Expansions Of Trigonometric Functions

Some Wolfram Alpha Features I Can T Achieve In Mathematica Mathematica Stack Exchange
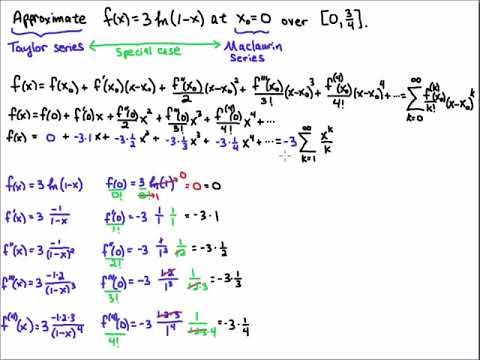
Taylor Series Expansion Of Natural Log Function Youtube

Taylor Series
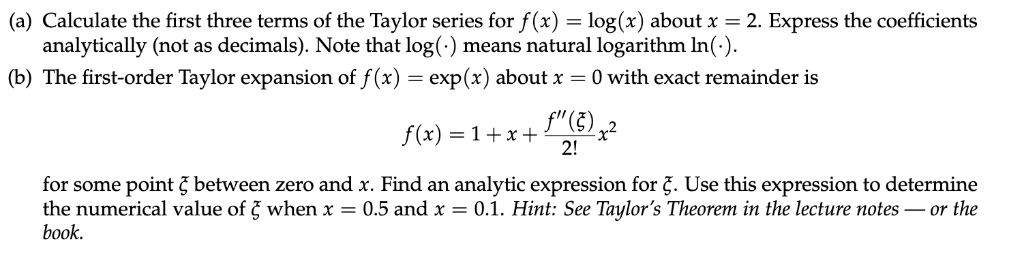
Solved A Calculate The First Three Terms Of The Taylor Chegg Com

Taylor Series From Wolfram Mathworld

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Maclaurin Series Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Is The Binomial Expansion Of Math 1 X 2 Math Quora

Consider The Following Two Taylor S Series Log 1 Chegg Com

Solved In 1 X Can Be Approximated Using The Following Chegg Com

Solved We Can Approximate The Natural Logarithm Using A T Chegg Com
Http Academic Uprm Edu Wrolke Esma6661 Hyp1 Html
Edumatth Weebly Com Uploads 1 3 1 9 Taylor Series Pdf

Maclaurin Series Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Taylor Series

Solved 1 10 Points The Taylor Series Approximation For Chegg Com

Logarithms Logs Log Ln Lg

Solved A Prove That The Taylor Series Of The Function F Chegg Com

Solved Derive The Tylor Series Expansion For Log 1 X Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcskxb6gvgapdft5ibnrins2t92z0suwezny Nudtzbvqw8wmwu8 Usqp Cau

The Natural Logarithm And Its Series Expansion 2 Ways Ln X 1 At 0 Youtube
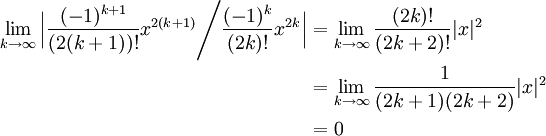
The Maclaurin Expansion Of Cos X The Infinite Series Module

Solved Compute The Taylor Series Up To 2 Nonzero Terms Chegg Com

Don T Understand Why This Binomial Expansion Is Not Valid For X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Natural Logarithm Series
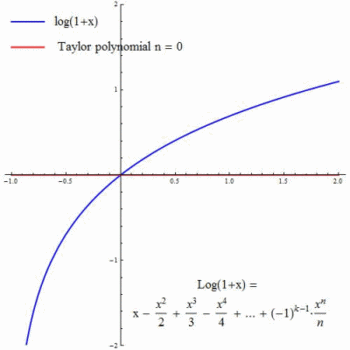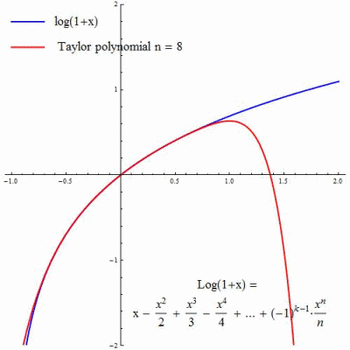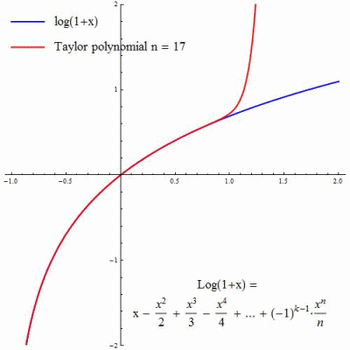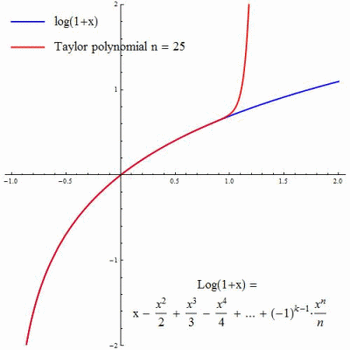
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrvq4n8spy0wjpphatpqtk03veinc7rsftbbg Usqp Cau

Help With Arithmetic On Basic Taylor Series Expansion Mathematics Stack Exchange
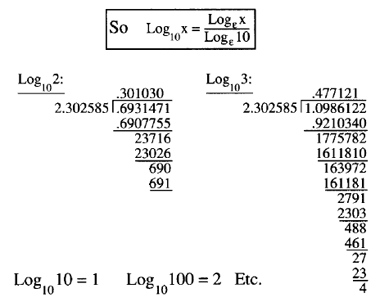
Logarithms Logs Log Ln Lg

Making Animation The Convergence Of The A Taylor Series Of Log 1 X Youtube

Solved Compute The Taylor Series Up To 2 Nonzero Terms Chegg Com
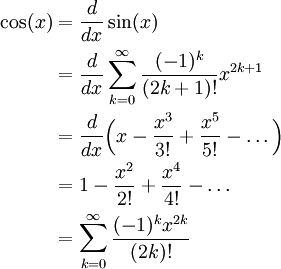
The Maclaurin Expansion Of Cos X The Infinite Series Module

Maclaurin Series Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Mathstat Slu Edu Clair Calc2 In Class Taylor Series Pdf
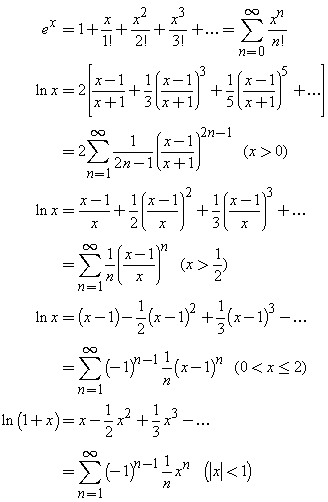
Series Expansions Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions

Solved 7 The Taylor Series Approximation For Log 1 Z Chegg Com

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Taylor Series Wikipedia

Cochranmath Taylor Series Of A Function By Equating Derivatives

Ap Calculus Review Taylor And Maclaurin Series Magoosh Blog High School
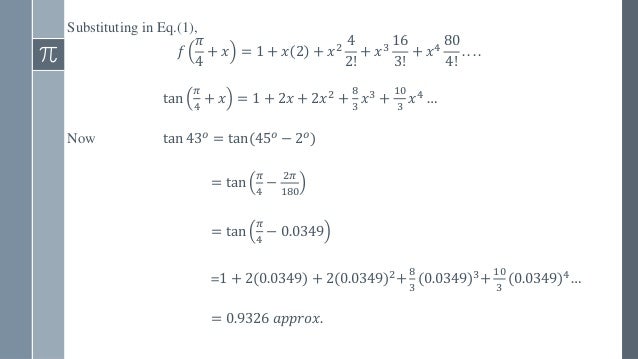
Power Series Taylor S And Maclaurin S Series
Q Tbn 3aand9gctbtxlnnayxhmuzrqoa Yvnh5szrbrtvfi8 V6gzgbt1ih96wxc Usqp Cau

Don T Understand Why This Binomial Expansion Is Not Valid For X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange

What Is The Limit Of Ln X 1 X When X Approaches 0 Quora

Taylor Series Wikipedia
2
Taylor Series

Implementing Taylor Series For Sine And Cosine In C Stack Overflow

Taylor Series Wikipedia

How Are Logs Calculated Quora
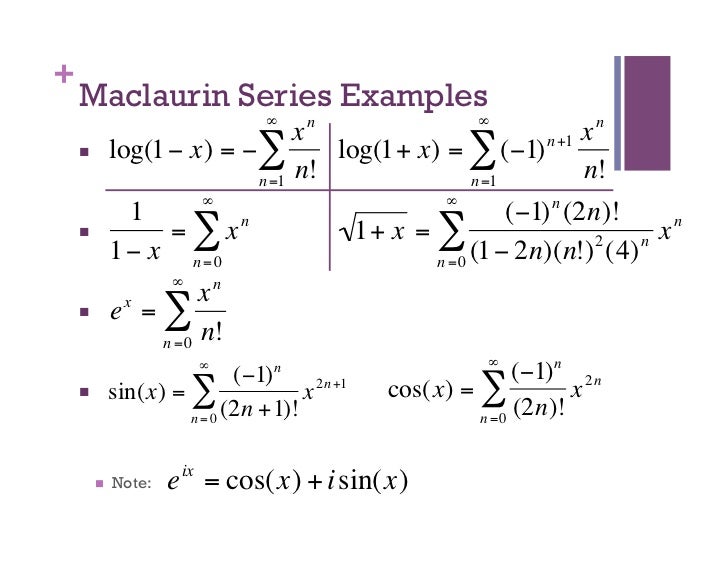
Taylor Series
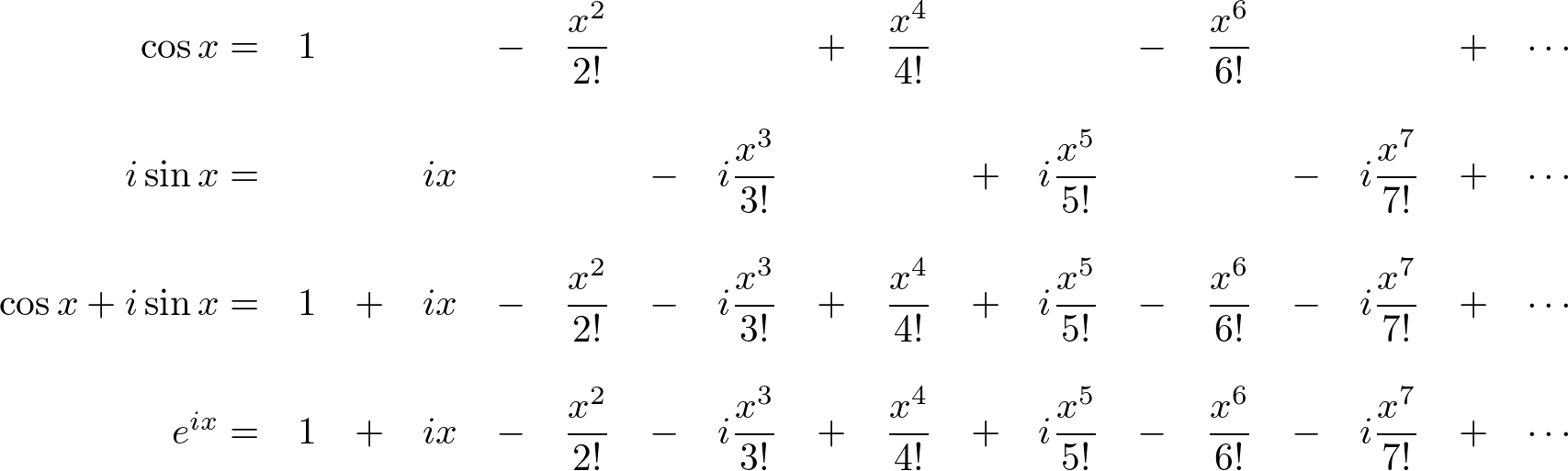
Euler S Equation

Taylor Series Expansions Of Exponential Functions
Q Tbn 3aand9gctsgw9vft4mnh Bijnjv0lau9ncbgfjor ujy9dpdwsb5rxwi Usqp Cau
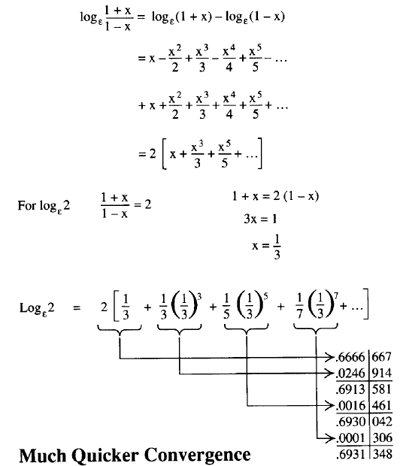
Logarithms Logs Log Ln Lg
2 Maclaurin Series

What Is The Correct Radius Of Convergence For Ln 1 X Mathematics Stack Exchange

Solved We Can Approximate The Natural Logarithm Using A T Chegg Com
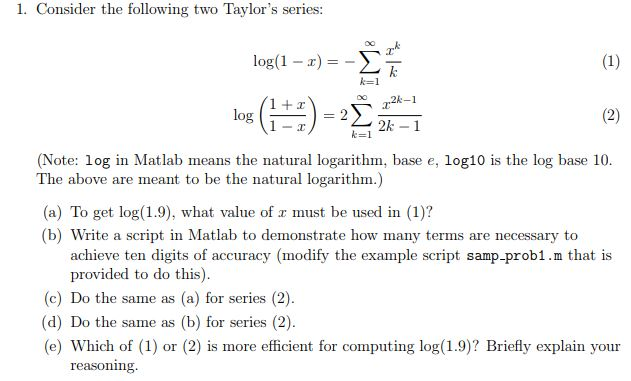
Solved 1 Consider The Following Two Taylor S Series Log Chegg Com

Maclaurin Series Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Natural Logarithm Wikipedia



